Las Vegas, a city known for its vibrant entertainment scene, is nestled in a unique geographical location that has a profound impact on its climate, infrastructure, and overall character. This article delves into the intriguing topic of Las Vegas elevation, examining its significance and exploring its far-reaching effects on various aspects of the city.
Las Vegas’s elevation, standing at a mere 2,162 feet (659 meters) above sea level, plays a crucial role in shaping the city’s arid desert climate, influencing temperature variations, humidity levels, and precipitation patterns. The low elevation also poses challenges for infrastructure development, requiring adaptations for water management, flood control, and transportation systems.
Introduction
Las Vegas, Nevada, is a city located in the southern part of the state, in the Mojave Desert. Geographically, it lies in the Las Vegas Valley, surrounded by mountains and desert landscapes. The city’s unique location has significantly influenced its development and characteristics, shaping its urban landscape, climate, and economic activities.
This article aims to analyze the elevation of Las Vegas and explore its impact on various aspects of the city, including its climate, infrastructure, and tourism industry. Understanding the city’s elevation provides valuable insights into its geographical features and the factors that have contributed to its growth and development.
Elevation of Las Vegas
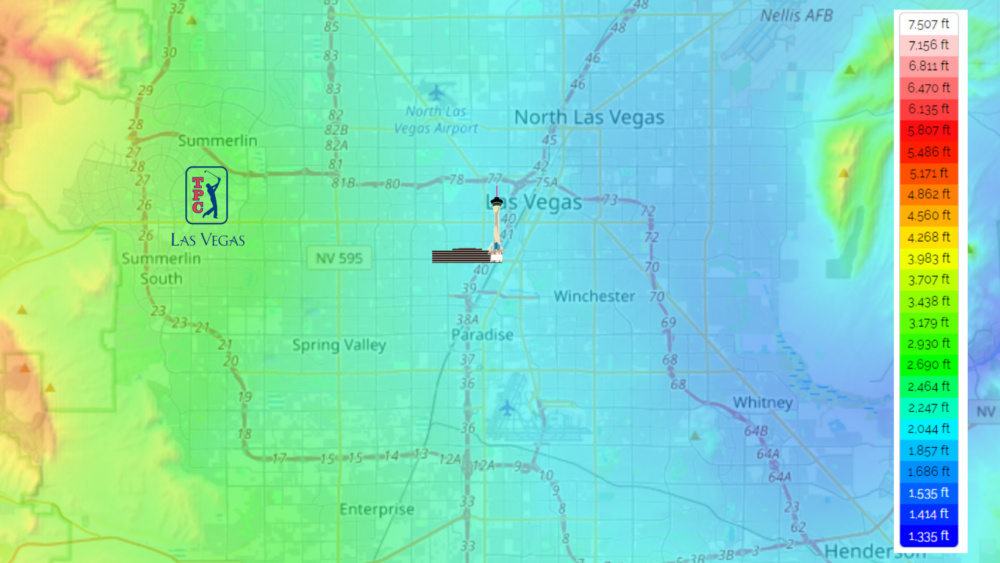
Las Vegas, known for its dazzling entertainment and vibrant atmosphere, is situated at a relatively low elevation compared to other major cities in the United States. Understanding the city’s elevation provides insights into its unique climate, geographical features, and infrastructure.
Exact Elevation
Las Vegas rests at an elevation of 2,030 feet (619 meters) above sea level. This elevation is significantly lower than many other metropolitan areas, such as Denver (5,280 feet) or Albuquerque (5,312 feet).
Significance of Low Elevation
The low elevation of Las Vegas has a profound impact on the city in several ways:
- Climate:The low elevation contributes to Las Vegas’s hot and dry desert climate. The city experiences scorching summers with average temperatures reaching up to 100 degrees Fahrenheit (38 degrees Celsius). Winters are generally mild, with average temperatures ranging from 40 to 60 degrees Fahrenheit (4 to 16 degrees Celsius).
- Geography:The low elevation allows for the formation of the Las Vegas Valley, which is surrounded by mountain ranges. The Spring Mountains to the west and the Sheep Range to the east protect the city from strong winds and severe weather events.
- Infrastructure:The city’s low elevation has influenced its infrastructure development. Las Vegas is known for its sprawling resorts, casinos, and entertainment venues, which have been built to accommodate the influx of tourists and visitors. The low elevation has also made it easier to construct and maintain transportation systems, such as the McCarran International Airport.
Impact on Climate
Las Vegas’s low elevation of 2,100 feet above sea level significantly influences its arid desert climate. Higher elevations generally result in cooler temperatures, increased humidity, and higher precipitation due to the adiabatic cooling effect. However, Las Vegas’s low elevation allows for warmer temperatures, lower humidity, and minimal precipitation.
Temperature Variations
The low elevation allows for a greater absorption of solar radiation, resulting in higher daytime temperatures. During the summer months, temperatures can reach up to 120°F (49°C). In contrast, during the winter months, temperatures can drop to as low as 30°F (-1°C).
This wide temperature range is a direct consequence of the city’s low elevation.
Humidity Levels
The low elevation also contributes to the city’s low humidity levels. As air rises, it cools and condenses, releasing moisture. However, due to Las Vegas’s low elevation, the air does not rise as high, resulting in less condensation and lower humidity levels.
The average humidity in Las Vegas is around 30%, which is significantly lower than the national average of 60%.
Precipitation Patterns, Las vegas elevation
The low elevation and arid climate of Las Vegas result in minimal precipitation. The city receives an average of only 4 inches of rain per year, making it one of the driest cities in the United States. The lack of precipitation is primarily due to the lack of moisture in the air and the city’s location in the rain shadow of the Sierra Nevada mountains.
Impact on Infrastructure
The low elevation of Las Vegas poses unique challenges for infrastructure development. The city is prone to flooding, and the lack of natural drainage systems makes it difficult to manage stormwater runoff. Additionally, the high water table can make it difficult to build underground infrastructure, such as subway systems and utility lines.
Water Management
The low elevation of Las Vegas makes it difficult to manage water resources. The city relies on groundwater for its water supply, but the water table is declining due to over-pumping. This has led to concerns about the long-term sustainability of the city’s water supply.
Flood Control
Las Vegas is prone to flooding, and the low elevation of the city makes it difficult to control floodwaters. The city has built a system of flood control channels and detention basins, but these are not always sufficient to prevent flooding during heavy rains.
Transportation Systems
The low elevation of Las Vegas can also impact transportation systems. The city’s airport is located in a low-lying area, and it is frequently closed due to flooding. Additionally, the city’s roads are often flooded during heavy rains, which can make it difficult to get around.
Tourism and Recreation
Las Vegas’s unique elevation has a significant impact on its tourism and outdoor activities. The city’s high elevation and dry climate make it an ideal destination for outdoor enthusiasts and those seeking a break from the heat.
The Las Vegas Strip, the city’s iconic entertainment and gambling district, is a popular destination for tourists from around the world. The Strip’s high-rise hotels, casinos, and attractions are well-suited to the city’s elevation, as the thin air allows for stunning views from the upper floors.
Red Rock Canyon
Red Rock Canyon, located just west of Las Vegas, is a popular destination for hiking, biking, and rock climbing. The canyon’s sandstone cliffs and formations are a unique and beautiful sight, and the elevation provides a challenging yet rewarding experience for outdoor enthusiasts.
Lake Mead
Lake Mead, the largest reservoir in the United States, is located just east of Las Vegas. The lake is a popular destination for boating, fishing, and swimming, and its elevation provides a cool and refreshing escape from the city’s heat.
Health and Well-being
Living in low-elevation areas can have certain health implications. Understanding these potential effects is essential for individuals residing in or considering moving to such regions.
Low-elevation areas are characterized by higher atmospheric pressure and oxygen concentration compared to higher altitudes. While this may seem beneficial, it can impact the body’s physiological functions.
Las Vegas, a vibrant city renowned for its dazzling lights and captivating entertainment, sits at an elevation of approximately 2,000 feet above sea level. This elevation contributes to the city’s unique climate and panoramic views. To explore Las Vegas’s vibrant landscape further, refer to this comprehensive las vegas airport map , providing detailed information on the city’s airport and surrounding areas.
Returning to the topic of elevation, Las Vegas’s altitude offers breathtaking vistas of the surrounding desert and mountain ranges, adding to the city’s allure as a captivating destination.
Respiratory Health
The increased atmospheric pressure in low-elevation areas can put additional strain on the respiratory system. The denser air requires more effort to breathe, leading to potential shortness of breath and reduced lung capacity.
Cardiovascular Function
The higher oxygen concentration in low-elevation areas can have both positive and negative effects on cardiovascular function. While it can improve oxygen delivery to tissues, it can also lead to increased heart rate and blood pressure. This can strain the cardiovascular system, especially in individuals with underlying heart conditions.
Overall Well-being
Living in low-elevation areas may also affect overall well-being. The reduced atmospheric pressure can lead to lower levels of melatonin production, which is a hormone that regulates sleep-wake cycles. This can result in sleep disturbances and decreased energy levels.
Comparisons with Other Cities
Las Vegas’s elevation of 2,165 feet (659 meters) places it among the highest major cities in the United States. This unique elevation has significant implications for the city’s climate, infrastructure, and overall character.
Elevation Comparison Table
To better understand Las Vegas’s elevation in context, here is a table comparing it to other major U.S. cities:| City | Elevation (feet) ||—|—|| Denver, Colorado | 5,280 || Albuquerque, New Mexico | 5,312 || Salt Lake City, Utah | 4,226 || Phoenix, Arizona | 1,117 || Los Angeles, California | 282 || New York City, New York | 33 || Chicago, Illinois | 606 || Houston, Texas | 59 || Miami, Florida | 6 |
Similarities and Differences
Las Vegas’s elevation is comparable to other cities in the Rocky Mountain region, such as Denver and Salt Lake City. These cities share similar challenges related to altitude sickness, respiratory issues, and UV exposure. However, Las Vegas’s relatively low elevation compared to cities like Denver and Albuquerque makes it less prone to severe weather events like snowstorms and extreme cold.On
the other hand, Las Vegas’s elevation is significantly higher than major coastal cities like Los Angeles, New York City, and Miami. This difference has a profound impact on the climate, with Las Vegas experiencing hotter and drier conditions due to its higher altitude and distance from large bodies of water.
Conclusion: Las Vegas Elevation
In conclusion, the elevation of Las Vegas has played a significant role in shaping its unique character. Its high elevation has contributed to its arid climate, necessitating the development of extensive infrastructure to support its population and tourism industry. The city’s location in a high-elevation desert has also impacted its health and well-being, with residents facing unique challenges related to heat and air quality.
The analysis highlights the importance of considering elevation when planning and managing urban areas. Understanding the implications of elevation can help cities mitigate potential risks and capitalize on the opportunities it presents. Las Vegas serves as an example of how elevation can influence a city’s development, climate, and overall well-being.
End of Discussion
In conclusion, Las Vegas’s elevation is an integral factor that has shaped the city’s unique identity. Its low elevation contributes to its arid climate, influences infrastructure development, affects tourism and outdoor activities, and may have implications for health and well-being.
Understanding the significance of elevation provides a deeper appreciation for the challenges and opportunities that have molded Las Vegas into the vibrant metropolis it is today.


